
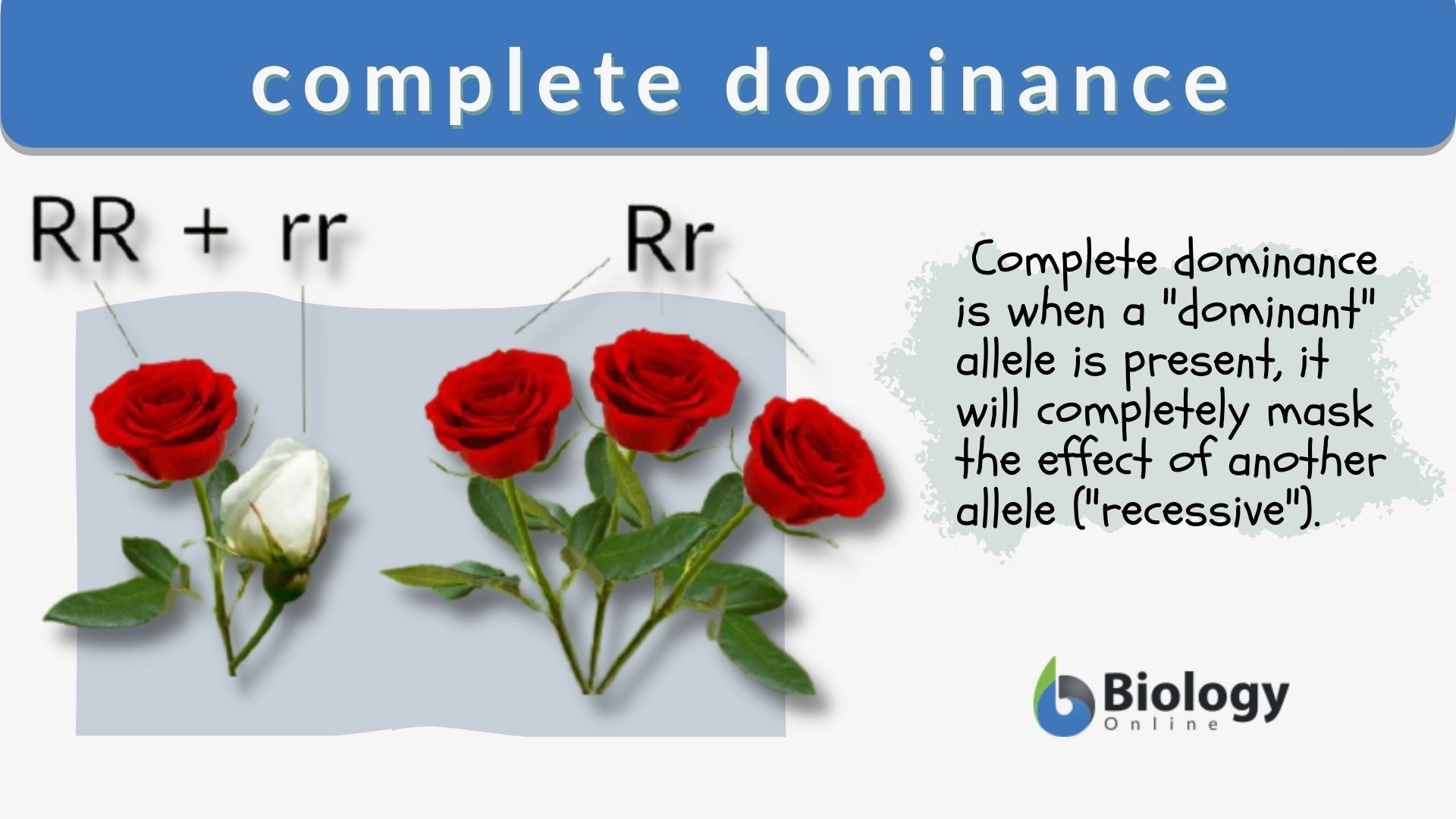
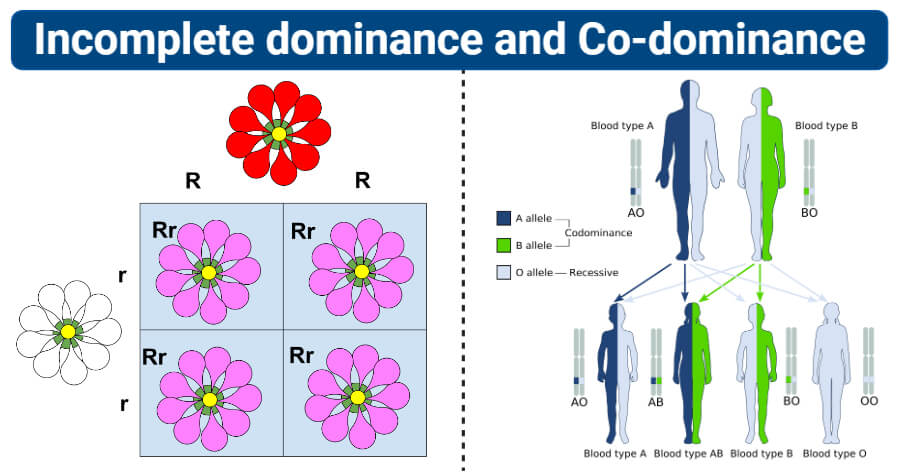
Some alleles can also be lethal, so their phenotype will never be observed. Genes on the X chromosome are X-linked, and males inherit and express only one allele for the gene (e.g., hemophilia, color-blindness). In humans, as in many animals and some plants, females have two X chromosomes, and males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. It is also common for more than two alleles of a gene to exist in a population (e.g., variations in sizes of pumpkins). Codominance describes the simultaneous expression of both of the alleles in the heterozygote (e.g., human blood types). For example, incomplete dominance describes situation in which the heterozygote exhibits a phenotype that is intermediate between the homozygous phenotypes (e.g., a pink-flowered offspring is produced from a cross between a red-flowered parent and a white-flowered parent). In other words, there are exceptions to Mendel’s model of inheritance. However, alleles do not always behave in dominant and recessive patterns. The recessive allele will only be observed in homozygous recessive individuals. For a gene whose expression is Mendelian ( Section 12.1), homozygous dominant and heterozygous organisms will look identical, that is, they will have different genotypes but the same phenotype. When diploid organisms carry the same alleles for a given trait, they are said to be homozygous for the genotype when they carry different alleles, they are said to be heterozygous. The organism’s underlying genetic makeup, that is, the combination of alleles, is called its genotype. The observable traits of an organism are referred to as its phenotype. These gene variations, for example, green peas versus yellow peas-are called alleles.ĭifferent alleles for a given gene in a diploid organism interact to express physical characteristics such as pea color in plants or hairline appearance in humans.
For cases in which a single gene controls a single characteristic, such as pea color, a diploid organism has genetic copies that may or may not encode the same version of the characteristic. Through meiosis, diploid organisms utilize meiosis to produce haploid (1 n) gametes that participate in fertilization. The genetic makeup of peas consists of two similar, or homologous-remember this term from Chapter 11-copies of each chromosome, one from each parent.

As we will explore in more detail in later chapters, the physical expression of characteristics is accomplished through the expression of genes-sequences of DNA-carried on chromosomes. The characteristics that Mendel evaluated in his pea plants were each expressed as one of two versions, or traits, for example, green peas versus yellow peas).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
